Health Insurance Claims Management Issues in Georgia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35945/gb.2023.16.003Keywords:
Insurance, Loss Management, Claim Adjustment, Claim RevisionAbstract
In the insurance market, the study of the adjustment of the amount requested by the medical organization is vital to ensure the stability of the industry and customer satisfaction. The research aims to analyze the adjustment process in the insurance market and to study the factors affecting the effective management of losses. According to research, the cost of the work performed by the medical institution is adjusted according to three main criteria: reimbursement, deadlines and discount. During adjustment, the following problems are identified: failure to consider the terms of the contract, neglect of its clauses, provision of disorderly documentation, and demand for compensation in an unscrupulous manner. The largest share of adjustments comes from hospitals, followed by pharmaceutical companies, outpatient clinics, and finally dental clinics. Although human health is important for medical organizations and insurance companies, their main goal is to increase revenues and make the right distribution for future purposes. It is important that insurance companies and medical institutions integrate software to eliminate problems, which will reduce deadlines, the risk of providing unnecessary services and other factors that cause adjustments.
Keywords: insurance, loss management, claim adjustment, claim revision
Introduction
One of the active participants in the medical market is an insurance company. The insurance industry protects individuals and businesses against various risks, such as accidents, natural disasters, and health emergencies (Freund et al., 2013).[1]
The assessment of insurance losses and the compensation process are important components of the management of the insurance sector. It involves settling an insurance claim, assessing losses and determining appropriate compensation (Irving et al., 2010).[2] An integral part of this process is adjusting the amount requested by the medical organization. The effectiveness of the adjustment process significantly affects the insurance industry’s ability to meet contractual obligations, maintain consumer confidence, and promote financial stability (Porter et al., 2022;[3] Sodzi-Tettey et al., 2012[4]). Claims adjustment requires a delicate balance between the interests of the insurer and the insured, ensuring fair settlement while avoiding fraudulent activity (Mahlow & Wagner, 2016;[5] Bhat & Reuben, 2002[6]).
In the insurance market, the study of the adjustment of the amount requested by the medical organization is vital to ensure the stability of the industry and customer satisfaction (Gowanit et al., 2016).[7] In this regard, it is relevant to study the various mechanisms involved in the adjustment process and their impact on the overall functioning of the insurance market. This enables insurers to develop effective loss management strategies, streamline operations and reduce financial losses. A transparent and timely adjustment process helps protect the insured’s rights, strengthens their confidence and ensures fast and efficient feedback on insurance claims.
The research aims to analyze the various mechanisms involved in the adjustment process in the insurance market and to study the factors affecting the effective management of losses.
Methodology
The qualitative research method was selected based on the specificity of the research. Representatives of the leading insurance companies and medical organizations participated in the research. As part of the qualitative research, in-depth interviews were conducted through a semi-structured questionnaire, which allowed us to get the most detailed information and analyze the identified problems. The statistical data of 2020-2023 on loss adjustments of one of the leading insurance companies was studied in the research process.
Results
According to 2020-2022 data, 1,282,472 individual cases were presented to insurance companies by clinics across Georgia, the total cost of which was determined at 58,228,529.85 GEL, of which 1,034,145.28 GEL was subject to correction, 216,058.09 GEL was subject to revision, the amount subject to compensation was made up 56,946,692.03 GEL.
The data for 2020 will be significantly different from the data of the following years, as the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the activities of insurance companies was directly reflected. In 2020, the number of cases was determined to be 298,192 individual cases, the total value of the invoices submitted by medical institutions amounted to 9,958,950.72 GEL, 135,421.21 GEL was subject to correction, 24,394.49 GEL to revision, and finally the reimbursed amount was 9,787,351.6 GEL.
According to the data of 2021, a total of 623,347 cases were registered in medical institutions; the presented cost was 20,826,752.42 GEL, of which the correction was 382,517.83 GEL, and the revision was 51,726.76 GEL, the value of the amount to be reimbursed was 20,382,290.51 GEL.
In 2022, the number of cases was determined to be 360,933 individual cases, the total cost of invoices submitted by medical institutions amounted to 27,442,826.71 GEL, 516,206.24 GEL were subject to correction, 139,936.84 GEL to revision, and finally the amount reimbursed amounted to 26,777,049.92 GEL.
The central part of the requested amount (56.92%) belongs to hospital services. 38.22% of the total requested amount was subject to correction. Accordingly, 57.03% of the reimbursed amount was transferred to hospitals.
Table 1: Claimed and adjusted amount to insurance companies, 2020-2022
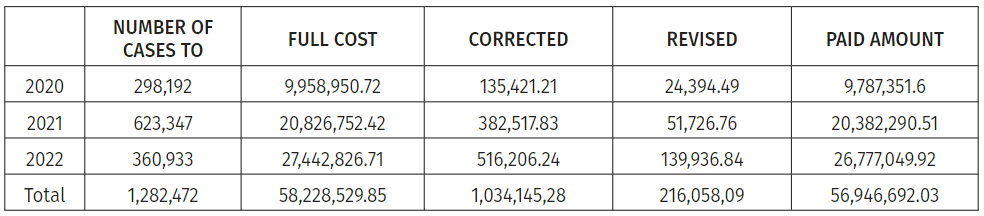
Table 2: Claimed and adjusted amounts to insurance companies by type of medical services, 2020-2022
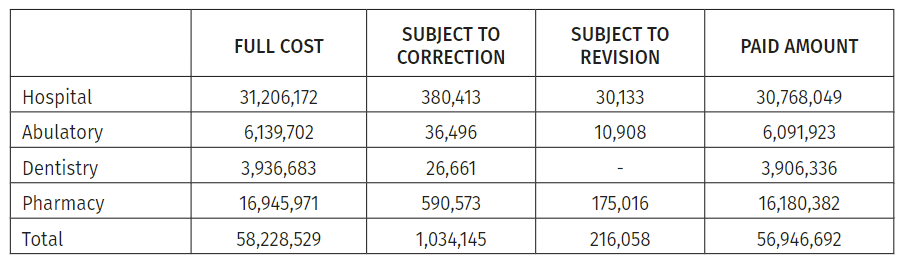
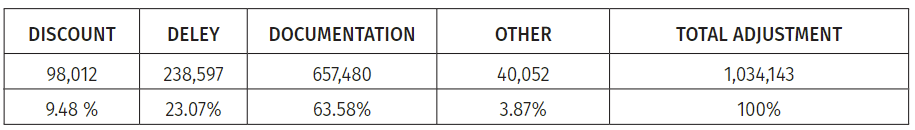
Table 3: Reasons for adjustment (in GEL) (2020-2022)
- The importance of having multiple provider clinics for an insurance company
Respondent I:
There are many reasons why it is important for an insurance company to have multiple provider clinics: Increased access to care, increased customer satisfaction, network adequacy and cost-effective services. Overall, having multiple provider clinics in its network allows an insurance company to offer a wider range of healthcare options, increase customer satisfaction, ensure network adequacy, and optimize the cost and quality of service provided to policyholders.
Respondent II:
An insurance company is a financial organization for which the number of insured persons and the use of the financial limits they establish are the priority. Having multiple providers provides many benefits to the insurance company. First of all, you have the opportunity to control the financing terms, that is, to postpone the loss, because if the insured goes to a non-provider clinic, in this case, the insurance company has to reimburse the amount when the insured sends the documents. But if it goes to the provider’s clinic, there is a transfer of funds in this case because the company has contractually defined deadlines for processing this performance. Accordingly, you must pay the amount not at the moment of service but within one or two months. Secondly, the more providers an insurance company has, the more it meets the insured’s needs.
Respondent III:
Many provider clinics allow us to offer policyholders a choice regarding different profiles, quality of service and geographic availability.
- Criteria for concluding contracts with medical institutions by insurance companies.
Respondent I:
Insurance companies enter into provider contracts with medical facilities based on several criteria that may vary depending on the specific company and its goals. However, insurance companies consider some common criteria when signing provider contracts. First, insurance companies evaluate whether a medical facility can meet their policyholder’s healthcare needs regarding geographic coverage and service delivery capabilities. Their goal is to ensure that their network includes a sufficient number and variety of providers to offer a comprehensive service. Insurance companies evaluate the quality of services provided by medical institutions. This assessment may include facility accreditation, certifications, patient treatment outcomes, patient satisfaction surveys, and compliance with regulatory standards. Insurers prefer to partner with medical organizations that adhere to high-quality standards.
- The main reasons for which the presented amount is adjusted.
Respondent I:
The main reasons for the correction of the amount presented by the medical institution are the failure to send the message to the insurer in urgent cases, the wrongly left message, or the correction due to the discount.
Respondent III:
The main reasons for the correction of the amount presented by the medical institution are incomplete documentation, provision of services with an invalid referral, missing identity documents, inconsistency with the diagnosis, rehospitalization of the insured during a short period of time from one medical institution to another, etc.
- Reasons for extending the time of payment after adjustment
Respondent I:
Because the medical institution wants to receive compensation on time and to respond within the terms set by the contract, it is in its interest to give a reasoned answer to the insurance company in time. After the argument submitted by the medical facility in response to the adjustment, the insurer may extend the process to extend the reimbursement period. Transfer of problem funds may take two or three months or more.
Respondent II:
Suppose it is impossible to clarify and agree on the adjustment details. In that case, the audit service is involved in eliminating the problem and trying to study the medical history on the spot. If the parties cannot reach an agreement after obtaining the supporting documents, the matter is transferred to the legal department, and then the cases are reviewed in the Supreme Court.
- Behavior of the insurance company and the medical institution in case of submission of performance and violation of deadlines
Respondent I:
The insurance company has the right not to accept the documentation submitted by the medical institution if it misses the terms stipulated in the contract. In case of delay in payment by the insurance company, the medical institution has the right to request information about this, request a report, and, if desired, terminate the contract with the insurance company.
- Frequency of breach of contract terms
Respondent I:
Any violation of the terms of the contract has a significant impact on the relationship between the medical institution and the insurance company, so both parties try to inform each other of each step, but even if something like this happens, at this time, both parties try to take into account the importance of each.
Respondent II:
It is quite common that what is controlled directly in the course of work based on the cases discovered they do not follow the pre-agreed deadlines and prices.
Respondent III:
It is common, but difficult, to strictly adhere to the terms of the contract when the provider clinic is popular with the insured.
- The main reasons for correcting the presented documentation
Respondent II:
There are many reasons for corrections in the submitted documentation of medical institutions, but they are mainly due to incomplete documentation, inappropriate diagnoses, provision of duplicate data, and violation of deadlines.
Respondent III:
It is very easy to find the reason for the correction, however, when the person is confused, we allow him to present the corrected documentation.
- Frequency of revision cases
Respondent III:
When any employee of the insurance company has questions and doubts about the presented documentation, there is a need for revision and auditors are sent to the clinic.
Discussion
Insurance companies, which have their medical facilities, refer to the family doctors they hire, sometimes obliging the insured to refer to their medical organizations, thus trying to avoid unnecessary costs. The submitted documentation is rarely corrected due to various violations in such cases.
On the other hand, insurance companies which do not have their medical facilities sign contracts with various medical facilities to provide uninterrupted services to their policyholders. In this case, insurance companies do not instruct family doctors to refer insured persons to any medical organization. However, insurance companies constantly provide policyholders with information about clinic bed capacity and try to offer high-quality medical services to avoid problems that increase policyholder dissatisfaction.
The research showed that the medical institution fulfils its obligation to provide medical services to insured persons in compliance with the conditions specified in the contract. In turn, the insurer fulfills the obligation to pay the cost of the medical services provided to the medical institution in accordance with the coverages/limits defined by the relevant policy and the medical service rates stipulated in the annexes of this agreement in a timely manner and fully. The contract concluded between the medical institution and the insurance organization is a lever, according to which they plan the relationship for at least one year. If the cooperation is stable and there are no serious violations by any of the parties, the contract continues in the following years on the basis of the agreement, under identical conditions, until it becomes fundamentally necessary to correct the clauses of the contract.
The contract includes both parties’ rights and obligations, which implies that the terms of submission or processing of the performed work, payment details, and prices play an important role. The medical institution undertakes to provide appropriate services to the insured, however, if there is a wrong medical action, incomplete presentation of the reporting documentation, failure to provide information to the insurer when the patient enters the clinic or within 24 hours at the latest, failure to consider the agreed limits and rates, in case of complications, delay of the insured for longer than the agreed time and other details, in this case, the insurance company reserves the right to check on the spot the fairness of the incurred loss or to request all the necessary documentation to be sure of the authenticity of the incident. The insurance company undertakes to provide the medical institution with information on the remaining limits of the insured, the scope of coverage and an explanation of the reimbursement or non-reimbursement of the incident.
The most important thing for medical institutions is increasing revenues and correctly budgeting. They aim to accumulate income as much as possible and distribute it correctly for future purposes. Financing of medical institutions is carried out by the state program of universal health care and funds received from private insurance companies.
The cost of the work performed by the medical institution is adjusted according to three main criteria: remuneration, terms and discount.
Compensation
The quality of cooperation between the medical institution and the insurance company is significantly affected by reimbursement. If either party is unhappy with the pay issue, it directly affects their relationship. When a medical facility does not provide appropriate, quality services to a particular insured, it has a negative impact on the insurance company. When there are frequent unfair claims made by the medical institution to the insurance company, the insurance company tries to redirect its insured to another acceptable medical institution. Reimbursement of medical expenses by the insurer is carried out in accordance with the tariffs determined by the contract. The medical institution offers a discount on the services in favor of the insurer, which is calculated from the full performance cost. Reimbursement includes several stages:
- After the end of the reporting month, all the necessary documentation of the insured persons who received services in a particular month and the total report of the relevant month will be submitted to the insurer.
- An act of acceptance and handover is drawn up, which is a document of commitment for both parties and therefore, a settlement is made. In case of loss or accidental destruction of the documentation provided according to this document, the medical institution is released from liability, and the insurance company has to fully compensate the case.
- From the signing of the act of acceptance to the expiration of the term specified in the contract, the insurance company processes the register and documentation of the submitted work, requests the missing documents, and then transfers the money to the medical institution.
- If the medical institution notifies the insurance company in writing about the missed events before the expiration of the processing period, the insurer is also obliged to accept the late submitted performance, process and pay compensation.
- As we have already mentioned, the cooperation between these two institutions is carried out according to the specially agreed prices, the medical institution has the right to change the prices, and if it informs the insurer about this in time, then the processing process will be carried out according to the new prices, but if the information about this was not provided in time and only In the process of processing, it became known to the insurer, in this case the insurance company reserves the right to process the documentation according to the old tariff.
Deadlines
The contract determines the terms of processing medical documentation. According to the contract terms, the processing time is generally set at 30 calendar days. The medical institution's identity card of the insured person, invoice, calculation form, notification, certified by the signature of the relevant authorized person and the institution’s seal must be submitted after the end of the reporting period, until the 10th of the following month. After receiving the documentation, the insurer has 20 working days to process the documentation and then another 10 days to make the payment. Within 20 days of processing, the medical institution must be notified in writing about the incompletely submitted documentation and allowed 14 calendar days after receiving the notification to correct the error and send the necessary documentation. To compensate for such cases, the insurance company is given an average of 15 working days to compensate the amount. As for adjusted cases, it is impossible to standardize the terms of their processing because each case is individual, requires individual investigation, and in many cases, the issue goes to court, which means that the issue of compensation may drag on for one, two or more months, even a year.
Discount
At the initial stage of the relationship between the medical institution and the insurance company, the medical institution provides the insurance company with the price of each service. At the next stage, an agreement on a price acceptable to both parties is made, therefore, the internal standard price of the medical institution is often adjusted by agreement with the insurer, and a price list is established. In this case, the medical institution distributes a discount to the insurance company with the relevant contract or creates a separate price list for it. In some cases, the medical institution has the right to change the prices, but the discount percentage determined by the contract remains unchanged.
If we consider the connection between adjustments and discounts as the main problem, the lack of information about price changes will be revealed. Often, the medical institution does not provide information on price changes to the insurance company on time. Currently, the insurance company reimburses the work performed by the medical institution at the old price. It should be noted that the discount applies only to referred patients and is not self-administered. In this case, the insurer will be obliged to compensate the insured according to the price established by the internal standard and not within the special price for him.
Conclusion
The purpose of the study was to determine the main problems arising in the process of relations between insurance companies and medical institutions, which, in many cases, become the reason for correction. In recent years, problems in the relationship between insurance companies and hospitals have been highlighted. Disputes are related to various factors, including rising healthcare costs, the handling of reimbursement disputes, and the complexity of insurance policies. These challenges have complicated partnerships between insurers and healthcare facilities, leading to a decline in trust.
One of the main problems remains the disagreement over pay rates. Insurance companies often negotiate lower rates to keep costs down, and hospitals try to get fair compensation to adequately cover their costs. These disagreements cause a severe financial blow to hospitals when the medical organization is forced to provide medical care to patients within limited resources and capacity.
In addition, insurance companies have the advantage of narrowing the area for the insured, removing certain hospitals from the list of providers, which limits the right of patients to receive medical services at the institution of their choice. One of the problematic issues is the complex and confusing nature of insurance policies. Policyholders often find it difficult to understand their coverage limits, which leads to unexpected costs and disputes. Hospitals try to adapt to this complex scheme and request funding, leading to payment delays and increasing the medical establishment’s administrative costs. These challenges create an inappropriate environment for the parties involved, contributing to strained relationships. To solve these problems, joint efforts are important. Improved communication and transparency between insurance companies and hospitals can help build trust and create a more corporate environment. Resolving conflicts requires engaging in open dialogue, sharing data, and setting clear expectations regarding reimbursement rates and coverage policies. In addition, both parties must work within regulatory frameworks that ensure fair rates of return and standardized insurance policies. Such measures can reduce the disparity between insurance companies and hospitals.
Problems in the relationship between insurance companies and hospitals in Georgia require a multifaceted approach that includes cooperation, transparency, and regulatory reforms. A more sustainable and patient-centred healthcare system can be created by addressing the root causes of these challenges and with a spirit of collaboration.
Recommendations
Based on the conducted research, the following recommendations may be issued to minimize the adjustment between medical institutions and insurance companies:
- To introduce integrated programs, where both parties will control the policyholder’s appeals, limits, diagnoses and compliance of the treatment method in the current process.
- It is appropriate to facilitate the training of administrative and medical personnel, considering the priorities, peculiarities and specifics of cooperation of the insurer and the medical organization.
- Continuous in-depth research of the most frequently corrected cases of the medical institution to find the causes and ways to solve them.
- Due to the abundance of data, it is advisable to start using artificial intelligence methods to analyze corrected cases without excessive effort.
- A clause on customer satisfaction should be added to the contracts concluded between insurance companies and medical institutions. Feedback received from each patient should be taken into account during reimbursement. A record like this will dramatically increase the level of customer satisfaction.
References
- Freund, T., Gondan, M., Rochon, J., ... Wensing, M., Szecsenyi, J. (2013). Comparison of physician referral and insurance claims data-based risk prediction as approaches to identify patients for care management in primary care: An observational study. BMC Family Practice, pp. 14, 157.
- Irving, A., Prager, A., Standley, C. A. (2010). customizable plan for effective claims management. J Healthc Risk Manag, 30 (2).
- Porter, C.N., Taylor, R., Harvey, A.C. (2022). Applying the asymmetric information management technique to insurance claims. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 36 (3), pp. 602–611.
- Sodzi-Tettey, S., Aikins, M., Awoonor-Williams, J.K., Agyepong, I.A. (2012). Challenges in provider payment under the Ghana National Health Insurance Scheme: a case study of claims management in two districts. Ghana medical journal, 46(4), pp. 189–199.
- Mahlow, N., Wagner, J. (2016). Evolution of Strategic Levers in Insurance Claims Management: An Industry Survey. Risk Management and Insurance Review, 19(2), pp. 197–223.
- Bhat, R., Reuben, E.B. (2002). Management of claims and reimbursements: The case of Mediclaim insurance policy. Vikalpa, 27(4), pp. 15–28.
- Gowanit, C., Thawesaengskulthai, N., Sophatsathit, P., Chaiyawat, T. (2016). Mobile claim management adoption in emerging insurance markets: An exploratory study in Thailand. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 34(1), pp. 110–130.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Globalization and Business

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









